
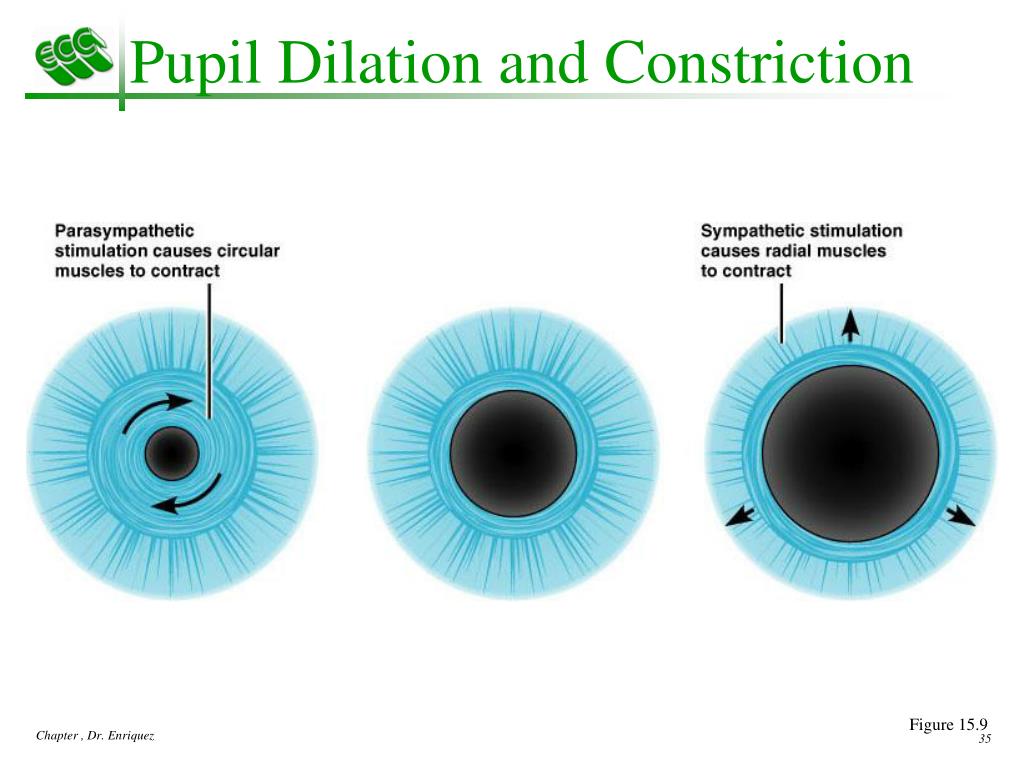
First-order neuron: sympathetic hypothalamic fibers → lateral intermediate columns of the spinal cord → ciliospinal center of Budge ( C8–T2).Contraction of the iris dilator muscle (surrounds the peripheral part of iris).Definition: dilation of the pupil ( > 4 mm in daylight).Pupillary control is mediated by both parasympatheticand sympatheticinnervation. Accommodation: preganglionic parasympathetic fibers from Edinger-Westphal nucleus travel with the oculomotor nerve → ciliary muscle contraction → increased lens convexity.Convergence: contraction of both medial rectus muscles → eyes look inward.Miosis: contraction of iris sphincter muscle.Accommodation reflex: The synkinetic constriction of the pupil ( miosis), convergence of the eyes, and accommodation of lens convexity in response to a suddenly closer object.Occurs via the medial recti muscles bilaterally and is mediated by the oculomotor nerve ( CN III).Simultaneous inward movement of both eyes to maintain focus on close objects (e.g., eyes crossing when looking at one's own nose).Constricted ciliary muscle → relaxed ciliary processes → curvature of lens increases.Relaxed ciliary muscle → tense ciliary processes → curvature of lens decreases.Changes occur via contraction of ciliary muscles and are mediated by the Edinger-Westphal nuclei bilaterally.

#Constricted pupil size meaning registration

Isocoria: the pupils of both eyes are the same size.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
